mirror of
https://github.com/encode/django-rest-framework.git
synced 2025-09-18 10:12:29 +03:00
Update branch with master
This commit is contained in:
commit
2e2b97872c
10
.travis.yml
10
.travis.yml
|
|
@ -21,11 +21,13 @@ matrix:
|
||||||
- { python: "3.7", env: DJANGO=2.2 }
|
- { python: "3.7", env: DJANGO=2.2 }
|
||||||
- { python: "3.7", env: DJANGO=master }
|
- { python: "3.7", env: DJANGO=master }
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- { python: "3.7", env: TOXENV=base }
|
- { python: "3.8", env: DJANGO=master }
|
||||||
- { python: "3.7", env: TOXENV=lint }
|
|
||||||
- { python: "3.7", env: TOXENV=docs }
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- python: "3.7"
|
- { python: "3.8", env: TOXENV=base }
|
||||||
|
- { python: "3.8", env: TOXENV=lint }
|
||||||
|
- { python: "3.8", env: TOXENV=docs }
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- python: "3.8"
|
||||||
env: TOXENV=dist
|
env: TOXENV=dist
|
||||||
script:
|
script:
|
||||||
- python setup.py bdist_wheel
|
- python setup.py bdist_wheel
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -17,11 +17,16 @@ other cache decorators such as [`cache_page`][page] and
|
||||||
[`vary_on_cookie`][cookie].
|
[`vary_on_cookie`][cookie].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```python
|
```python
|
||||||
|
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
|
||||||
|
from django.views.decorators.cache import cache_page
|
||||||
|
from django.views.decorators.vary import vary_on_cookie
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from rest_framework.response import Response
|
from rest_framework.response import Response
|
||||||
from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
||||||
from rest_framework import viewsets
|
from rest_framework import viewsets
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class UserViewSet(viewsets.Viewset):
|
|
||||||
|
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ViewSet):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Cache requested url for each user for 2 hours
|
# Cache requested url for each user for 2 hours
|
||||||
@method_decorator(cache_page(60*60*2))
|
@method_decorator(cache_page(60*60*2))
|
||||||
|
|
@ -32,6 +37,7 @@ class UserViewSet(viewsets.Viewset):
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return Response(content)
|
return Response(content)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class PostView(APIView):
|
class PostView(APIView):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Cache page for the requested url
|
# Cache page for the requested url
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -713,7 +713,7 @@ the coordinate pair:
|
||||||
fields = ['label', 'coordinates']
|
fields = ['label', 'coordinates']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Note that this example doesn't handle validation. Partly for that reason, in a
|
Note that this example doesn't handle validation. Partly for that reason, in a
|
||||||
real project, the coordinate nesting might be better handled with a nested serialiser
|
real project, the coordinate nesting might be better handled with a nested serializer
|
||||||
using `source='*'`, with two `IntegerField` instances, each with their own `source`
|
using `source='*'`, with two `IntegerField` instances, each with their own `source`
|
||||||
pointing to the relevant field.
|
pointing to the relevant field.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -746,7 +746,7 @@ suitable for updating our target object. With `source='*'`, the return from
|
||||||
('y_coordinate', 4),
|
('y_coordinate', 4),
|
||||||
('x_coordinate', 3)])
|
('x_coordinate', 3)])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For completeness lets do the same thing again but with the nested serialiser
|
For completeness lets do the same thing again but with the nested serializer
|
||||||
approach suggested above:
|
approach suggested above:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class NestedCoordinateSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
|
class NestedCoordinateSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -768,14 +768,14 @@ declarations. It's our `NestedCoordinateSerializer` that takes `source='*'`.
|
||||||
Our new `DataPointSerializer` exhibits the same behaviour as the custom field
|
Our new `DataPointSerializer` exhibits the same behaviour as the custom field
|
||||||
approach.
|
approach.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Serialising:
|
Serializing:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
>>> out_serializer = DataPointSerializer(instance)
|
>>> out_serializer = DataPointSerializer(instance)
|
||||||
>>> out_serializer.data
|
>>> out_serializer.data
|
||||||
ReturnDict([('label', 'testing'),
|
ReturnDict([('label', 'testing'),
|
||||||
('coordinates', OrderedDict([('x', 1), ('y', 2)]))])
|
('coordinates', OrderedDict([('x', 1), ('y', 2)]))])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Deserialising:
|
Deserializing:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
>>> in_serializer = DataPointSerializer(data=data)
|
>>> in_serializer = DataPointSerializer(data=data)
|
||||||
>>> in_serializer.is_valid()
|
>>> in_serializer.is_valid()
|
||||||
|
|
@ -802,8 +802,8 @@ But we also get the built-in validation for free:
|
||||||
{'x': ['A valid integer is required.'],
|
{'x': ['A valid integer is required.'],
|
||||||
'y': ['A valid integer is required.']})])
|
'y': ['A valid integer is required.']})])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For this reason, the nested serialiser approach would be the first to try. You
|
For this reason, the nested serializer approach would be the first to try. You
|
||||||
would use the custom field approach when the nested serialiser becomes infeasible
|
would use the custom field approach when the nested serializer becomes infeasible
|
||||||
or overly complex.
|
or overly complex.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -378,10 +378,6 @@ If you need to generic PUT-as-create behavior you may want to include something
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The following third party packages provide additional generic view implementations.
|
The following third party packages provide additional generic view implementations.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Django REST Framework bulk
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The [django-rest-framework-bulk package][django-rest-framework-bulk] implements generic view mixins as well as some common concrete generic views to allow to apply bulk operations via API requests.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Django Rest Multiple Models
|
## Django Rest Multiple Models
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[Django Rest Multiple Models][django-rest-multiple-models] provides a generic view (and mixin) for sending multiple serialized models and/or querysets via a single API request.
|
[Django Rest Multiple Models][django-rest-multiple-models] provides a generic view (and mixin) for sending multiple serialized models and/or querysets via a single API request.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -394,5 +390,4 @@ The [django-rest-framework-bulk package][django-rest-framework-bulk] implements
|
||||||
[RetrieveModelMixin]: #retrievemodelmixin
|
[RetrieveModelMixin]: #retrievemodelmixin
|
||||||
[UpdateModelMixin]: #updatemodelmixin
|
[UpdateModelMixin]: #updatemodelmixin
|
||||||
[DestroyModelMixin]: #destroymodelmixin
|
[DestroyModelMixin]: #destroymodelmixin
|
||||||
[django-rest-framework-bulk]: https://github.com/miki725/django-rest-framework-bulk
|
|
||||||
[django-rest-multiple-models]: https://github.com/MattBroach/DjangoRestMultipleModels
|
[django-rest-multiple-models]: https://github.com/MattBroach/DjangoRestMultipleModels
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -245,7 +245,9 @@ This field is always read-only.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Nested relationships
|
# Nested relationships
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Nested relationships can be expressed by using serializers as fields.
|
As opposed to previously discussed _references_ to another entity, the referred entity can instead also be embedded or _nested_
|
||||||
|
in the representation of the object that refers to it.
|
||||||
|
Such nested relationships can be expressed by using serializers as fields.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If the field is used to represent a to-many relationship, you should add the `many=True` flag to the serializer field.
|
If the field is used to represent a to-many relationship, you should add the `many=True` flag to the serializer field.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ If a client sends a request with a content-type that cannot be parsed then a `Un
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Content negotiation
|
# Content negotiation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The request exposes some properties that allow you to determine the result of the content negotiation stage. This allows you to implement behaviour such as selecting a different serialisation schemes for different media types.
|
The request exposes some properties that allow you to determine the result of the content negotiation stage. This allows you to implement behaviour such as selecting a different serialization schemes for different media types.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## .accepted_renderer
|
## .accepted_renderer
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -94,5 +94,5 @@ As with any other `TemplateResponse`, this method is called to render the serial
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You won't typically need to call `.render()` yourself, as it's handled by Django's standard response cycle.
|
You won't typically need to call `.render()` yourself, as it's handled by Django's standard response cycle.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[cite]: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/stable/template-response/
|
[cite]: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/stable/ref/template-response/
|
||||||
[statuscodes]: status-codes.md
|
[statuscodes]: status-codes.md
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ The `get_schema_view()` helper takes the following keyword arguments:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* `title`: May be used to provide a descriptive title for the schema definition.
|
* `title`: May be used to provide a descriptive title for the schema definition.
|
||||||
* `description`: Longer descriptive text.
|
* `description`: Longer descriptive text.
|
||||||
* `version`: The version of the API. Defaults to `0.1.0`.
|
* `version`: The version of the API.
|
||||||
* `url`: May be used to pass a canonical base URL for the schema.
|
* `url`: May be used to pass a canonical base URL for the schema.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
schema_view = get_schema_view(
|
schema_view = get_schema_view(
|
||||||
|
|
@ -90,6 +90,7 @@ The `get_schema_view()` helper takes the following keyword arguments:
|
||||||
url='https://www.example.org/api/',
|
url='https://www.example.org/api/',
|
||||||
urlconf='myproject.urls'
|
urlconf='myproject.urls'
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* `patterns`: List of url patterns to limit the schema introspection to. If you
|
* `patterns`: List of url patterns to limit the schema introspection to. If you
|
||||||
only want the `myproject.api` urls to be exposed in the schema:
|
only want the `myproject.api` urls to be exposed in the schema:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -114,7 +115,6 @@ The `get_schema_view()` helper takes the following keyword arguments:
|
||||||
* `renderer_classes`: May be used to pass the set of renderer classes that can
|
* `renderer_classes`: May be used to pass the set of renderer classes that can
|
||||||
be used to render the API root endpoint.
|
be used to render the API root endpoint.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Customizing Schema Generation
|
## Customizing Schema Generation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You may customize schema generation at the level of the schema as a whole, or
|
You may customize schema generation at the level of the schema as a whole, or
|
||||||
|
|
@ -154,7 +154,7 @@ Returns a dictionary that represents the OpenAPI schema:
|
||||||
The `request` argument is optional, and may be used if you want to apply
|
The `request` argument is optional, and may be used if you want to apply
|
||||||
per-user permissions to the resulting schema generation.
|
per-user permissions to the resulting schema generation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This is a good point to override if you want to customise the generated
|
This is a good point to override if you want to customize the generated
|
||||||
dictionary, for example to add custom
|
dictionary, for example to add custom
|
||||||
[specification extensions][openapi-specification-extensions].
|
[specification extensions][openapi-specification-extensions].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -176,21 +176,20 @@ for each view, allowed method, and path.
|
||||||
**Note**: For basic `APIView` subclasses, default introspection is essentially
|
**Note**: For basic `APIView` subclasses, default introspection is essentially
|
||||||
limited to the URL kwarg path parameters. For `GenericAPIView`
|
limited to the URL kwarg path parameters. For `GenericAPIView`
|
||||||
subclasses, which includes all the provided class based views, `AutoSchema` will
|
subclasses, which includes all the provided class based views, `AutoSchema` will
|
||||||
attempt to introspect serialiser, pagination and filter fields, as well as
|
attempt to introspect serializer, pagination and filter fields, as well as
|
||||||
provide richer path field descriptions. (The key hooks here are the relevant
|
provide richer path field descriptions. (The key hooks here are the relevant
|
||||||
`GenericAPIView` attributes and methods: `get_serializer`, `pagination_class`,
|
`GenericAPIView` attributes and methods: `get_serializer`, `pagination_class`,
|
||||||
`filter_backends` and so on.)
|
`filter_backends` and so on.)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
---
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In order to customise the operation generation, you should provide an `AutoSchema` subclass, overriding `get_operation()` as you need:
|
In order to customize the operation generation, you should provide an `AutoSchema` subclass, overriding `get_operation()` as you need:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
||||||
from rest_framework.schemas.openapi import AutoSchema
|
from rest_framework.schemas.openapi import AutoSchema
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class CustomSchema(AutoSchema):
|
class CustomSchema(AutoSchema):
|
||||||
def get_link(...):
|
def get_operation(...):
|
||||||
# Implement custom introspection here (or in other sub-methods)
|
# Implement custom introspection here (or in other sub-methods)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class CustomView(APIView):
|
class CustomView(APIView):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -218,4 +217,4 @@ project you may adjust `settings.DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS` appropriately.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[openapi]: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification
|
[openapi]: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification
|
||||||
[openapi-specification-extensions]: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#specification-extensions
|
[openapi-specification-extensions]: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#specification-extensions
|
||||||
[openapi-operation]: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#operationObject
|
[openapi-operation]: https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#operationObject
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -887,10 +887,10 @@ To implement a read-only serializer using the `BaseSerializer` class, we just ne
|
||||||
It's simple to create a read-only serializer for converting `HighScore` instances into primitive data types.
|
It's simple to create a read-only serializer for converting `HighScore` instances into primitive data types.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class HighScoreSerializer(serializers.BaseSerializer):
|
class HighScoreSerializer(serializers.BaseSerializer):
|
||||||
def to_representation(self, obj):
|
def to_representation(self, instance):
|
||||||
return {
|
return {
|
||||||
'score': obj.score,
|
'score': instance.score,
|
||||||
'player_name': obj.player_name
|
'player_name': instance.player_name
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We can now use this class to serialize single `HighScore` instances:
|
We can now use this class to serialize single `HighScore` instances:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -945,10 +945,10 @@ Here's a complete example of our previous `HighScoreSerializer`, that's been upd
|
||||||
'player_name': player_name
|
'player_name': player_name
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def to_representation(self, obj):
|
def to_representation(self, instance):
|
||||||
return {
|
return {
|
||||||
'score': obj.score,
|
'score': instance.score,
|
||||||
'player_name': obj.player_name
|
'player_name': instance.player_name
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def create(self, validated_data):
|
def create(self, validated_data):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -965,10 +965,10 @@ The following class is an example of a generic serializer that can handle coerci
|
||||||
A read-only serializer that coerces arbitrary complex objects
|
A read-only serializer that coerces arbitrary complex objects
|
||||||
into primitive representations.
|
into primitive representations.
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
def to_representation(self, obj):
|
def to_representation(self, instance):
|
||||||
output = {}
|
output = {}
|
||||||
for attribute_name in dir(obj):
|
for attribute_name in dir(instance):
|
||||||
attribute = getattr(obj, attribute_name)
|
attribute = getattr(instance, attribute_name)
|
||||||
if attribute_name.startswith('_'):
|
if attribute_name.startswith('_'):
|
||||||
# Ignore private attributes.
|
# Ignore private attributes.
|
||||||
pass
|
pass
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1010,7 +1010,7 @@ Some reasons this might be useful include...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The signatures for these methods are as follows:
|
The signatures for these methods are as follows:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### `.to_representation(self, obj)`
|
#### `.to_representation(self, instance)`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Takes the object instance that requires serialization, and should return a primitive representation. Typically this means returning a structure of built-in Python datatypes. The exact types that can be handled will depend on the render classes you have configured for your API.
|
Takes the object instance that requires serialization, and should return a primitive representation. Typically this means returning a structure of built-in Python datatypes. The exact types that can be handled will depend on the render classes you have configured for your API.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ Default: `'rest_framework.negotiation.DefaultContentNegotiation'`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A view inspector class that will be used for schema generation.
|
A view inspector class that will be used for schema generation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Default: `'rest_framework.schemas.AutoSchema'`
|
Default: `'rest_framework.schemas.openapi.AutoSchema'`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
---
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -132,12 +132,12 @@ This scheme requires the client to specify the version as part of the URL path.
|
||||||
Your URL conf must include a pattern that matches the version with a `'version'` keyword argument, so that this information is available to the versioning scheme.
|
Your URL conf must include a pattern that matches the version with a `'version'` keyword argument, so that this information is available to the versioning scheme.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
urlpatterns = [
|
urlpatterns = [
|
||||||
url(
|
re_path(
|
||||||
r'^(?P<version>(v1|v2))/bookings/$',
|
r'^(?P<version>(v1|v2))/bookings/$',
|
||||||
bookings_list,
|
bookings_list,
|
||||||
name='bookings-list'
|
name='bookings-list'
|
||||||
),
|
),
|
||||||
url(
|
re_path(
|
||||||
r'^(?P<version>(v1|v2))/bookings/(?P<pk>[0-9]+)/$',
|
r'^(?P<version>(v1|v2))/bookings/(?P<pk>[0-9]+)/$',
|
||||||
bookings_detail,
|
bookings_detail,
|
||||||
name='bookings-detail'
|
name='bookings-detail'
|
||||||
|
|
@ -158,14 +158,14 @@ In the following example we're giving a set of views two different possible URL
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# bookings/urls.py
|
# bookings/urls.py
|
||||||
urlpatterns = [
|
urlpatterns = [
|
||||||
url(r'^$', bookings_list, name='bookings-list'),
|
re_path(r'^$', bookings_list, name='bookings-list'),
|
||||||
url(r'^(?P<pk>[0-9]+)/$', bookings_detail, name='bookings-detail')
|
re_path(r'^(?P<pk>[0-9]+)/$', bookings_detail, name='bookings-detail')
|
||||||
]
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# urls.py
|
# urls.py
|
||||||
urlpatterns = [
|
urlpatterns = [
|
||||||
url(r'^v1/bookings/', include('bookings.urls', namespace='v1')),
|
re_path(r'^v1/bookings/', include('bookings.urls', namespace='v1')),
|
||||||
url(r'^v2/bookings/', include('bookings.urls', namespace='v2'))
|
re_path(r'^v2/bookings/', include('bookings.urls', namespace='v2'))
|
||||||
]
|
]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Both `URLPathVersioning` and `NamespaceVersioning` are reasonable if you just need a simple versioning scheme. The `URLPathVersioning` approach might be better suitable for small ad-hoc projects, and the `NamespaceVersioning` is probably easier to manage for larger projects.
|
Both `URLPathVersioning` and `NamespaceVersioning` are reasonable if you just need a simple versioning scheme. The `URLPathVersioning` approach might be better suitable for small ad-hoc projects, and the `NamespaceVersioning` is probably easier to manage for larger projects.
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ urlpatterns = [
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Customization
|
### Customization
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For customizations that you want to apply across the the entire API, you can subclass `rest_framework.schemas.openapi.SchemaGenerator` and provide it as an argument
|
For customizations that you want to apply across the entire API, you can subclass `rest_framework.schemas.openapi.SchemaGenerator` and provide it as an argument
|
||||||
to the `generateschema` command or `get_schema_view()` helper function.
|
to the `generateschema` command or `get_schema_view()` helper function.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
For specific per-view customizations, you can subclass `AutoSchema`,
|
For specific per-view customizations, you can subclass `AutoSchema`,
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -195,7 +195,6 @@ If `@tomchristie` ceases to participate in the project then `@j4mie` has respons
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The following issues still need to be addressed:
|
The following issues still need to be addressed:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* [Consider moving the repo into a proper GitHub organization][github-org].
|
|
||||||
* Ensure `@jamie` has back-up access to the `django-rest-framework.org` domain setup and admin.
|
* Ensure `@jamie` has back-up access to the `django-rest-framework.org` domain setup and admin.
|
||||||
* Document ownership of the [live example][sandbox] API.
|
* Document ownership of the [live example][sandbox] API.
|
||||||
* Document ownership of the [mailing list][mailing-list] and IRC channel.
|
* Document ownership of the [mailing list][mailing-list] and IRC channel.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -206,6 +205,5 @@ The following issues still need to be addressed:
|
||||||
[transifex-project]: https://www.transifex.com/projects/p/django-rest-framework/
|
[transifex-project]: https://www.transifex.com/projects/p/django-rest-framework/
|
||||||
[transifex-client]: https://pypi.org/project/transifex-client/
|
[transifex-client]: https://pypi.org/project/transifex-client/
|
||||||
[translation-memory]: http://docs.transifex.com/guides/tm#let-tm-automatically-populate-translations
|
[translation-memory]: http://docs.transifex.com/guides/tm#let-tm-automatically-populate-translations
|
||||||
[github-org]: https://github.com/encode/django-rest-framework/issues/2162
|
|
||||||
[sandbox]: https://restframework.herokuapp.com/
|
[sandbox]: https://restframework.herokuapp.com/
|
||||||
[mailing-list]: https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/django-rest-framework
|
[mailing-list]: https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/django-rest-framework
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -222,11 +222,11 @@ Be sure to upgrade to Python 3 before upgrading to Django REST Framework 3.10.
|
||||||
def perform_create(self, serializer):
|
def perform_create(self, serializer):
|
||||||
serializer.save(owner=self.request.user)
|
serializer.save(owner=self.request.user)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Alternatively you may override `save()` or `create()` or `update()` on the serialiser as appropriate.
|
Alternatively you may override `save()` or `create()` or `update()` on the serializer as appropriate.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* Correct allow_null behaviour when required=False [#5888][gh5888]
|
* Correct allow_null behaviour when required=False [#5888][gh5888]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Without an explicit `default`, `allow_null` implies a default of `null` for outgoing serialisation. Previously such
|
Without an explicit `default`, `allow_null` implies a default of `null` for outgoing serialization. Previously such
|
||||||
fields were being skipped when read-only or otherwise not required.
|
fields were being skipped when read-only or otherwise not required.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Possible backwards compatibility break** if you were relying on such fields being excluded from the outgoing
|
**Possible backwards compatibility break** if you were relying on such fields being excluded from the outgoing
|
||||||
|
|
@ -464,7 +464,7 @@ Be sure to upgrade to Python 3 before upgrading to Django REST Framework 3.10.
|
||||||
* Deprecated `exclude_from_schema` on `APIView` and `api_view` decorator. Set `schema = None` or `@schema(None)` as appropriate. [#5422][gh5422]
|
* Deprecated `exclude_from_schema` on `APIView` and `api_view` decorator. Set `schema = None` or `@schema(None)` as appropriate. [#5422][gh5422]
|
||||||
* Timezone-aware `DateTimeField`s now respect active or default `timezone` during serialization, instead of always using UTC. [#5435][gh5435]
|
* Timezone-aware `DateTimeField`s now respect active or default `timezone` during serialization, instead of always using UTC. [#5435][gh5435]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Resolves inconsistency whereby instances were serialised with supplied datetime for `create` but UTC for `retrieve`. [#3732][gh3732]
|
Resolves inconsistency whereby instances were serialized with supplied datetime for `create` but UTC for `retrieve`. [#3732][gh3732]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
**Possible backwards compatibility break** if you were relying on datetime strings being UTC. Have client interpret datetimes or [set default or active timezone (docs)][djangodocs-set-timezone] to UTC if needed.
|
**Possible backwards compatibility break** if you were relying on datetime strings being UTC. Have client interpret datetimes or [set default or active timezone (docs)][djangodocs-set-timezone] to UTC if needed.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -222,7 +222,6 @@ To submit new content, [open an issue][drf-create-issue] or [create a pull reque
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Views
|
### Views
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* [djangorestframework-bulk][djangorestframework-bulk] - Implements generic view mixins as well as some common concrete generic views to allow to apply bulk operations via API requests.
|
|
||||||
* [django-rest-multiple-models][django-rest-multiple-models] - Provides a generic view (and mixin) for sending multiple serialized models and/or querysets via a single API request.
|
* [django-rest-multiple-models][django-rest-multiple-models] - Provides a generic view (and mixin) for sending multiple serialized models and/or querysets via a single API request.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Routers
|
### Routers
|
||||||
|
|
@ -254,8 +253,7 @@ To submit new content, [open an issue][drf-create-issue] or [create a pull reque
|
||||||
### Misc
|
### Misc
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* [cookiecutter-django-rest][cookiecutter-django-rest] - A cookiecutter template that takes care of the setup and configuration so you can focus on making your REST apis awesome.
|
* [cookiecutter-django-rest][cookiecutter-django-rest] - A cookiecutter template that takes care of the setup and configuration so you can focus on making your REST apis awesome.
|
||||||
* [djangorestrelationalhyperlink][djangorestrelationalhyperlink] - A hyperlinked serialiser that can can be used to alter relationships via hyperlinks, but otherwise like a hyperlink model serializer.
|
* [djangorestrelationalhyperlink][djangorestrelationalhyperlink] - A hyperlinked serializer that can can be used to alter relationships via hyperlinks, but otherwise like a hyperlink model serializer.
|
||||||
* [django-rest-swagger][django-rest-swagger] - An API documentation generator for Swagger UI.
|
|
||||||
* [django-rest-framework-proxy][django-rest-framework-proxy] - Proxy to redirect incoming request to another API server.
|
* [django-rest-framework-proxy][django-rest-framework-proxy] - Proxy to redirect incoming request to another API server.
|
||||||
* [gaiarestframework][gaiarestframework] - Utils for django-rest-framework
|
* [gaiarestframework][gaiarestframework] - Utils for django-rest-framework
|
||||||
* [drf-extensions][drf-extensions] - A collection of custom extensions
|
* [drf-extensions][drf-extensions] - A collection of custom extensions
|
||||||
|
|
@ -273,6 +271,7 @@ To submit new content, [open an issue][drf-create-issue] or [create a pull reque
|
||||||
* [django-rest-witchcraft][django-rest-witchcraft] - Provides DRF integration with SQLAlchemy with SQLAlchemy model serializers/viewsets and a bunch of other goodies
|
* [django-rest-witchcraft][django-rest-witchcraft] - Provides DRF integration with SQLAlchemy with SQLAlchemy model serializers/viewsets and a bunch of other goodies
|
||||||
* [djangorestframework-mvt][djangorestframework-mvt] - An extension for creating views that serve Postgres data as Map Box Vector Tiles.
|
* [djangorestframework-mvt][djangorestframework-mvt] - An extension for creating views that serve Postgres data as Map Box Vector Tiles.
|
||||||
* [drf-viewset-profiler][drf-viewset-profiler] - Lib to profile all methods from a viewset line by line.
|
* [drf-viewset-profiler][drf-viewset-profiler] - Lib to profile all methods from a viewset line by line.
|
||||||
|
* [djangorestframework-features][djangorestframework-features] - Advanced schema generation and more based on named features.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[cite]: http://www.software-ecosystems.com/Software_Ecosystems/Ecosystems.html
|
[cite]: http://www.software-ecosystems.com/Software_Ecosystems/Ecosystems.html
|
||||||
[cookiecutter]: https://github.com/jpadilla/cookiecutter-django-rest-framework
|
[cookiecutter]: https://github.com/jpadilla/cookiecutter-django-rest-framework
|
||||||
|
|
@ -306,7 +305,6 @@ To submit new content, [open an issue][drf-create-issue] or [create a pull reque
|
||||||
[djangorestframework-hstore]: https://github.com/djangonauts/django-rest-framework-hstore
|
[djangorestframework-hstore]: https://github.com/djangonauts/django-rest-framework-hstore
|
||||||
[drf-compound-fields]: https://github.com/estebistec/drf-compound-fields
|
[drf-compound-fields]: https://github.com/estebistec/drf-compound-fields
|
||||||
[django-extra-fields]: https://github.com/Hipo/drf-extra-fields
|
[django-extra-fields]: https://github.com/Hipo/drf-extra-fields
|
||||||
[djangorestframework-bulk]: https://github.com/miki725/django-rest-framework-bulk
|
|
||||||
[django-rest-multiple-models]: https://github.com/MattBroach/DjangoRestMultipleModels
|
[django-rest-multiple-models]: https://github.com/MattBroach/DjangoRestMultipleModels
|
||||||
[drf-nested-routers]: https://github.com/alanjds/drf-nested-routers
|
[drf-nested-routers]: https://github.com/alanjds/drf-nested-routers
|
||||||
[wq.db.rest]: https://wq.io/docs/about-rest
|
[wq.db.rest]: https://wq.io/docs/about-rest
|
||||||
|
|
@ -318,7 +316,6 @@ To submit new content, [open an issue][drf-create-issue] or [create a pull reque
|
||||||
[djangorestframework-rapidjson]: https://github.com/allisson/django-rest-framework-rapidjson
|
[djangorestframework-rapidjson]: https://github.com/allisson/django-rest-framework-rapidjson
|
||||||
[djangorestframework-chain]: https://github.com/philipn/django-rest-framework-chain
|
[djangorestframework-chain]: https://github.com/philipn/django-rest-framework-chain
|
||||||
[djangorestrelationalhyperlink]: https://github.com/fredkingham/django_rest_model_hyperlink_serializers_project
|
[djangorestrelationalhyperlink]: https://github.com/fredkingham/django_rest_model_hyperlink_serializers_project
|
||||||
[django-rest-swagger]: https://github.com/marcgibbons/django-rest-swagger
|
|
||||||
[django-rest-framework-proxy]: https://github.com/eofs/django-rest-framework-proxy
|
[django-rest-framework-proxy]: https://github.com/eofs/django-rest-framework-proxy
|
||||||
[gaiarestframework]: https://github.com/AppsFuel/gaiarestframework
|
[gaiarestframework]: https://github.com/AppsFuel/gaiarestframework
|
||||||
[drf-extensions]: https://github.com/chibisov/drf-extensions
|
[drf-extensions]: https://github.com/chibisov/drf-extensions
|
||||||
|
|
@ -356,3 +353,4 @@ To submit new content, [open an issue][drf-create-issue] or [create a pull reque
|
||||||
[djangorestframework-mvt]: https://github.com/corteva/djangorestframework-mvt
|
[djangorestframework-mvt]: https://github.com/corteva/djangorestframework-mvt
|
||||||
[django-rest-framework-guardian]: https://github.com/rpkilby/django-rest-framework-guardian
|
[django-rest-framework-guardian]: https://github.com/rpkilby/django-rest-framework-guardian
|
||||||
[drf-viewset-profiler]: https://github.com/fvlima/drf-viewset-profiler
|
[drf-viewset-profiler]: https://github.com/fvlima/drf-viewset-profiler
|
||||||
|
[djangorestframework-features]: https://github.com/cloudcode-hungary/django-rest-framework-features/
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ each view, allowed method and path.)
|
||||||
**Note**: For basic `APIView` subclasses, default introspection is essentially
|
**Note**: For basic `APIView` subclasses, default introspection is essentially
|
||||||
limited to the URL kwarg path parameters. For `GenericAPIView`
|
limited to the URL kwarg path parameters. For `GenericAPIView`
|
||||||
subclasses, which includes all the provided class based views, `AutoSchema` will
|
subclasses, which includes all the provided class based views, `AutoSchema` will
|
||||||
attempt to introspect serialiser, pagination and filter fields, as well as
|
attempt to introspect serializer, pagination and filter fields, as well as
|
||||||
provide richer path field descriptions. (The key hooks here are the relevant
|
provide richer path field descriptions. (The key hooks here are the relevant
|
||||||
`GenericAPIView` attributes and methods: `get_serializer`, `pagination_class`,
|
`GenericAPIView` attributes and methods: `get_serializer`, `pagination_class`,
|
||||||
`filter_backends` and so on.)
|
`filter_backends` and so on.)
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB |
Binary file not shown.
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 75 KiB |
|
|
@ -140,56 +140,6 @@ This also translates into a very useful interactive documentation viewer in the
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
---
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Django REST Swagger
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Marc Gibbons' [Django REST Swagger][django-rest-swagger] integrates REST framework with the [Swagger][swagger] API documentation tool. The package produces well presented API documentation, and includes interactive tools for testing API endpoints.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Django REST Swagger supports REST framework versions 2.3 and above.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Mark is also the author of the [REST Framework Docs][rest-framework-docs] package which offers clean, simple autogenerated documentation for your API but is deprecated and has moved to Django REST Swagger.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This package is fully documented, well supported, and comes highly recommended.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
![Screenshot - Django REST Swagger][image-django-rest-swagger]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### DRF AutoDocs
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Oleksander Mashianovs' [DRF Auto Docs][drfautodocs-repo] automated api renderer.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Collects almost all the code you written into documentation effortlessly.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Supports:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
* functional view docs
|
|
||||||
* tree-like structure
|
|
||||||
* Docstrings:
|
|
||||||
* markdown
|
|
||||||
* preserve space & newlines
|
|
||||||
* formatting with nice syntax
|
|
||||||
* Fields:
|
|
||||||
* choices rendering
|
|
||||||
* help_text (to specify SerializerMethodField output, etc)
|
|
||||||
* smart read_only/required rendering
|
|
||||||
* Endpoint properties:
|
|
||||||
* filter_backends
|
|
||||||
* authentication_classes
|
|
||||||
* permission_classes
|
|
||||||
* extra url params(GET params)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
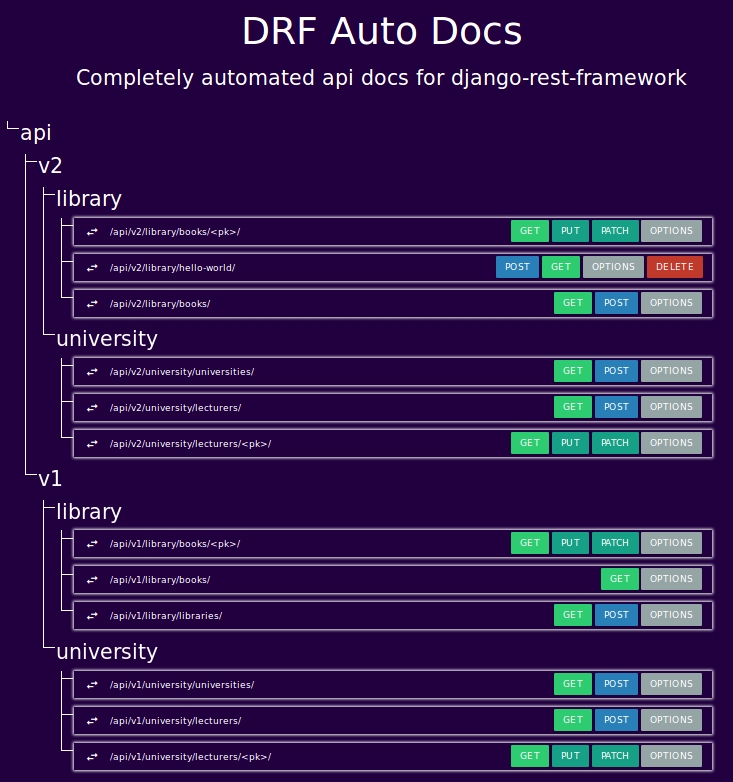
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Apiary
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
There are various other online tools and services for providing API documentation. One notable service is [Apiary][apiary]. With Apiary, you describe your API using a simple markdown-like syntax. The generated documentation includes API interaction, a mock server for testing & prototyping, and various other tools.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
![Screenshot - Apiary][image-apiary]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
---
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Self describing APIs
|
## Self describing APIs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The browsable API that REST framework provides makes it possible for your API to be entirely self describing. The documentation for each API endpoint can be provided simply by visiting the URL in your browser.
|
The browsable API that REST framework provides makes it possible for your API to be entirely self describing. The documentation for each API endpoint can be provided simply by visiting the URL in your browser.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -221,7 +171,7 @@ If the python `Markdown` library is installed, then [markdown syntax][markdown]
|
||||||
[ref]: http://example.com/activating-accounts
|
[ref]: http://example.com/activating-accounts
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Note that when using viewsets the basic docstring is used for all generated views. To provide descriptions for each view, such as for the the list and retrieve views, use docstring sections as described in [Schemas as documentation: Examples][schemas-examples].
|
Note that when using viewsets the basic docstring is used for all generated views. To provide descriptions for each view, such as for the list and retrieve views, use docstring sections as described in [Schemas as documentation: Examples][schemas-examples].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### The `OPTIONS` method
|
#### The `OPTIONS` method
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -253,22 +203,17 @@ In this approach, rather than documenting the available API endpoints up front,
|
||||||
To implement a hypermedia API you'll need to decide on an appropriate media type for the API, and implement a custom renderer and parser for that media type. The [REST, Hypermedia & HATEOAS][hypermedia-docs] section of the documentation includes pointers to background reading, as well as links to various hypermedia formats.
|
To implement a hypermedia API you'll need to decide on an appropriate media type for the API, and implement a custom renderer and parser for that media type. The [REST, Hypermedia & HATEOAS][hypermedia-docs] section of the documentation includes pointers to background reading, as well as links to various hypermedia formats.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[cite]: https://roy.gbiv.com/untangled/2008/rest-apis-must-be-hypertext-driven
|
[cite]: https://roy.gbiv.com/untangled/2008/rest-apis-must-be-hypertext-driven
|
||||||
[drf-yasg]: https://github.com/axnsan12/drf-yasg/
|
|
||||||
[image-drf-yasg]: ../img/drf-yasg.png
|
|
||||||
[drfautodocs-repo]: https://github.com/iMakedonsky/drf-autodocs
|
|
||||||
[django-rest-swagger]: https://github.com/marcgibbons/django-rest-swagger
|
|
||||||
[swagger]: https://swagger.io/
|
|
||||||
[open-api]: https://openapis.org/
|
|
||||||
[rest-framework-docs]: https://github.com/marcgibbons/django-rest-framework-docs
|
|
||||||
[apiary]: https://apiary.io/
|
|
||||||
[markdown]: https://daringfireball.net/projects/markdown/syntax
|
|
||||||
[hypermedia-docs]: rest-hypermedia-hateoas.md
|
[hypermedia-docs]: rest-hypermedia-hateoas.md
|
||||||
[image-django-rest-swagger]: ../img/django-rest-swagger.png
|
|
||||||
[image-apiary]: ../img/apiary.png
|
|
||||||
[image-self-describing-api]: ../img/self-describing.png
|
|
||||||
[metadata-docs]: ../api-guide/metadata/
|
[metadata-docs]: ../api-guide/metadata/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[schemas-examples]: ../api-guide/schemas/#examples
|
[schemas-examples]: ../api-guide/schemas/#examples
|
||||||
[swagger-ui]: https://swagger.io/tools/swagger-ui/
|
|
||||||
[redoc]: https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[image-drf-yasg]: ../img/drf-yasg.png
|
||||||
|
[image-self-describing-api]: ../img/self-describing.png
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[drf-yasg]: https://github.com/axnsan12/drf-yasg/
|
||||||
|
[markdown]: https://daringfireball.net/projects/markdown/syntax
|
||||||
|
[open-api]: https://openapis.org/
|
||||||
|
[redoc]: https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc
|
||||||
|
[swagger]: https://swagger.io/
|
||||||
|
[swagger-ui]: https://swagger.io/tools/swagger-ui/
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||||
# PEP8 code linting, which we run on all commits.
|
# PEP8 code linting, which we run on all commits.
|
||||||
flake8==3.5.0
|
flake8==3.7.8
|
||||||
flake8-tidy-imports==1.1.0
|
flake8-tidy-imports==3.0.0
|
||||||
pycodestyle==2.3.1
|
pycodestyle==2.5.0
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Sort and lint imports
|
# Sort and lint imports
|
||||||
isort==4.3.3
|
isort==4.3.21
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ ______ _____ _____ _____ __
|
||||||
__title__ = 'Django REST framework'
|
__title__ = 'Django REST framework'
|
||||||
__version__ = '3.10.3'
|
__version__ = '3.10.3'
|
||||||
__author__ = 'Tom Christie'
|
__author__ = 'Tom Christie'
|
||||||
__license__ = 'BSD 2-Clause'
|
__license__ = 'BSD 3-Clause'
|
||||||
__copyright__ = 'Copyright 2011-2019 Encode OSS Ltd'
|
__copyright__ = 'Copyright 2011-2019 Encode OSS Ltd'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Version synonym
|
# Version synonym
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1062,9 +1062,7 @@ class DecimalField(Field):
|
||||||
except decimal.DecimalException:
|
except decimal.DecimalException:
|
||||||
self.fail('invalid')
|
self.fail('invalid')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Check for NaN. It is the only value that isn't equal to itself,
|
if value.is_nan():
|
||||||
# so we can use this to identify NaN values.
|
|
||||||
if value != value:
|
|
||||||
self.fail('invalid')
|
self.fail('invalid')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Check for infinity and negative infinity.
|
# Check for infinity and negative infinity.
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -47,12 +47,12 @@ class Hyperlink(str):
|
||||||
in some contexts, or render as a plain URL in others.
|
in some contexts, or render as a plain URL in others.
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
def __new__(cls, url, obj):
|
def __new__(cls, url, obj):
|
||||||
ret = str.__new__(cls, url)
|
ret = super().__new__(cls, url)
|
||||||
ret.obj = obj
|
ret.obj = obj
|
||||||
return ret
|
return ret
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __getnewargs__(self):
|
def __getnewargs__(self):
|
||||||
return(str(self), self.name,)
|
return (str(self), self.name)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@property
|
@property
|
||||||
def name(self):
|
def name(self):
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -23,8 +23,8 @@ Other access should target the submodules directly
|
||||||
from rest_framework.settings import api_settings
|
from rest_framework.settings import api_settings
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from . import coreapi, openapi
|
from . import coreapi, openapi
|
||||||
from .inspectors import DefaultSchema # noqa
|
|
||||||
from .coreapi import AutoSchema, ManualSchema, SchemaGenerator # noqa
|
from .coreapi import AutoSchema, ManualSchema, SchemaGenerator # noqa
|
||||||
|
from .inspectors import DefaultSchema # noqa
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_schema_view(
|
def get_schema_view(
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1,26 +1,18 @@
|
||||||
import re
|
|
||||||
import warnings
|
import warnings
|
||||||
from collections import Counter, OrderedDict
|
from collections import Counter, OrderedDict
|
||||||
from urllib import parse
|
from urllib import parse
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from django.db import models
|
from django.db import models
|
||||||
from django.utils.encoding import force_str, smart_text
|
from django.utils.encoding import force_str
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from rest_framework import exceptions, serializers
|
from rest_framework import exceptions, serializers
|
||||||
from rest_framework.compat import coreapi, coreschema, uritemplate
|
from rest_framework.compat import coreapi, coreschema, uritemplate
|
||||||
from rest_framework.settings import api_settings
|
from rest_framework.settings import api_settings
|
||||||
from rest_framework.utils import formatting
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from .generators import BaseSchemaGenerator
|
from .generators import BaseSchemaGenerator
|
||||||
from .inspectors import ViewInspector
|
from .inspectors import ViewInspector
|
||||||
from .utils import get_pk_description, is_list_view
|
from .utils import get_pk_description, is_list_view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Used in _get_description_section()
|
|
||||||
# TODO: ???: move up to base.
|
|
||||||
header_regex = re.compile('^[a-zA-Z][0-9A-Za-z_]*:')
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Generator #
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def common_path(paths):
|
def common_path(paths):
|
||||||
split_paths = [path.strip('/').split('/') for path in paths]
|
split_paths = [path.strip('/').split('/') for path in paths]
|
||||||
|
|
@ -397,44 +389,6 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
description=description
|
description=description
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_description(self, path, method):
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
Determine a link description.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This will be based on the method docstring if one exists,
|
|
||||||
or else the class docstring.
|
|
||||||
"""
|
|
||||||
view = self.view
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
method_name = getattr(view, 'action', method.lower())
|
|
||||||
method_docstring = getattr(view, method_name, None).__doc__
|
|
||||||
if method_docstring:
|
|
||||||
# An explicit docstring on the method or action.
|
|
||||||
return self._get_description_section(view, method.lower(), formatting.dedent(smart_text(method_docstring)))
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
return self._get_description_section(view, getattr(view, 'action', method.lower()), view.get_view_description())
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def _get_description_section(self, view, header, description):
|
|
||||||
lines = [line for line in description.splitlines()]
|
|
||||||
current_section = ''
|
|
||||||
sections = {'': ''}
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for line in lines:
|
|
||||||
if header_regex.match(line):
|
|
||||||
current_section, seperator, lead = line.partition(':')
|
|
||||||
sections[current_section] = lead.strip()
|
|
||||||
else:
|
|
||||||
sections[current_section] += '\n' + line
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# TODO: SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES appears here and in `SchemaGenerator.get_keys`
|
|
||||||
coerce_method_names = api_settings.SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES
|
|
||||||
if header in sections:
|
|
||||||
return sections[header].strip()
|
|
||||||
if header in coerce_method_names:
|
|
||||||
if coerce_method_names[header] in sections:
|
|
||||||
return sections[coerce_method_names[header]].strip()
|
|
||||||
return sections[''].strip()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_path_fields(self, path, method):
|
def get_path_fields(self, path, method):
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
Return a list of `coreapi.Field` instances corresponding to any
|
Return a list of `coreapi.Field` instances corresponding to any
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ class BaseSchemaGenerator(object):
|
||||||
# Set by 'SCHEMA_COERCE_PATH_PK'.
|
# Set by 'SCHEMA_COERCE_PATH_PK'.
|
||||||
coerce_path_pk = None
|
coerce_path_pk = None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __init__(self, title=None, url=None, description=None, patterns=None, urlconf=None, version=''):
|
def __init__(self, title=None, url=None, description=None, patterns=None, urlconf=None, version=None):
|
||||||
if url and not url.endswith('/'):
|
if url and not url.endswith('/'):
|
||||||
url += '/'
|
url += '/'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -3,9 +3,13 @@ inspectors.py # Per-endpoint view introspection
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
See schemas.__init__.py for package overview.
|
See schemas.__init__.py for package overview.
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
import re
|
||||||
from weakref import WeakKeyDictionary
|
from weakref import WeakKeyDictionary
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
from django.utils.encoding import smart_text
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from rest_framework.settings import api_settings
|
from rest_framework.settings import api_settings
|
||||||
|
from rest_framework.utils import formatting
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class ViewInspector:
|
class ViewInspector:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -15,6 +19,9 @@ class ViewInspector:
|
||||||
Provide subclass for per-view schema generation
|
Provide subclass for per-view schema generation
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Used in _get_description_section()
|
||||||
|
header_regex = re.compile('^[a-zA-Z][0-9A-Za-z_]*:')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __init__(self):
|
def __init__(self):
|
||||||
self.instance_schemas = WeakKeyDictionary()
|
self.instance_schemas = WeakKeyDictionary()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -62,6 +69,45 @@ class ViewInspector:
|
||||||
def view(self):
|
def view(self):
|
||||||
self._view = None
|
self._view = None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def get_description(self, path, method):
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
Determine a path description.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This will be based on the method docstring if one exists,
|
||||||
|
or else the class docstring.
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
view = self.view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
method_name = getattr(view, 'action', method.lower())
|
||||||
|
method_docstring = getattr(view, method_name, None).__doc__
|
||||||
|
if method_docstring:
|
||||||
|
# An explicit docstring on the method or action.
|
||||||
|
return self._get_description_section(view, method.lower(), formatting.dedent(smart_text(method_docstring)))
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
return self._get_description_section(view, getattr(view, 'action', method.lower()),
|
||||||
|
view.get_view_description())
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def _get_description_section(self, view, header, description):
|
||||||
|
lines = [line for line in description.splitlines()]
|
||||||
|
current_section = ''
|
||||||
|
sections = {'': ''}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for line in lines:
|
||||||
|
if self.header_regex.match(line):
|
||||||
|
current_section, separator, lead = line.partition(':')
|
||||||
|
sections[current_section] = lead.strip()
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
sections[current_section] += '\n' + line
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# TODO: SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES appears here and in `SchemaGenerator.get_keys`
|
||||||
|
coerce_method_names = api_settings.SCHEMA_COERCE_METHOD_NAMES
|
||||||
|
if header in sections:
|
||||||
|
return sections[header].strip()
|
||||||
|
if header in coerce_method_names:
|
||||||
|
if coerce_method_names[header] in sections:
|
||||||
|
return sections[coerce_method_names[header]].strip()
|
||||||
|
return sections[''].strip()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class DefaultSchema(ViewInspector):
|
class DefaultSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
"""Allows overriding AutoSchema using DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS setting"""
|
"""Allows overriding AutoSchema using DEFAULT_SCHEMA_CLASS setting"""
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||||
import warnings
|
import warnings
|
||||||
|
from operator import attrgetter
|
||||||
from urllib.parse import urljoin
|
from urllib.parse import urljoin
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from django.core.validators import (
|
from django.core.validators import (
|
||||||
|
|
@ -8,7 +9,7 @@ from django.core.validators import (
|
||||||
from django.db import models
|
from django.db import models
|
||||||
from django.utils.encoding import force_str
|
from django.utils.encoding import force_str
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from rest_framework import exceptions, serializers
|
from rest_framework import exceptions, renderers, serializers
|
||||||
from rest_framework.compat import uritemplate
|
from rest_framework.compat import uritemplate
|
||||||
from rest_framework.fields import _UnvalidatedField, empty
|
from rest_framework.fields import _UnvalidatedField, empty
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -16,15 +17,14 @@ from .generators import BaseSchemaGenerator
|
||||||
from .inspectors import ViewInspector
|
from .inspectors import ViewInspector
|
||||||
from .utils import get_pk_description, is_list_view
|
from .utils import get_pk_description, is_list_view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Generator
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class SchemaGenerator(BaseSchemaGenerator):
|
class SchemaGenerator(BaseSchemaGenerator):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def get_info(self):
|
def get_info(self):
|
||||||
|
# Title and version are required by openapi specification 3.x
|
||||||
info = {
|
info = {
|
||||||
'title': self.title,
|
'title': self.title or '',
|
||||||
'version': self.version,
|
'version': self.version or ''
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if self.description is not None:
|
if self.description is not None:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -78,7 +78,9 @@ class SchemaGenerator(BaseSchemaGenerator):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
content_types = ['application/json']
|
request_media_types = []
|
||||||
|
response_media_types = []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
method_mapping = {
|
method_mapping = {
|
||||||
'get': 'Retrieve',
|
'get': 'Retrieve',
|
||||||
'post': 'Create',
|
'post': 'Create',
|
||||||
|
|
@ -91,6 +93,7 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
operation = {}
|
operation = {}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
operation['operationId'] = self._get_operation_id(path, method)
|
operation['operationId'] = self._get_operation_id(path, method)
|
||||||
|
operation['description'] = self.get_description(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
parameters = []
|
parameters = []
|
||||||
parameters += self._get_path_parameters(path, method)
|
parameters += self._get_path_parameters(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -209,7 +212,7 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
if not is_list_view(path, method, view):
|
if not is_list_view(path, method, view):
|
||||||
return []
|
return []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
paginator = self._get_pagninator()
|
paginator = self._get_paginator()
|
||||||
if not paginator:
|
if not paginator:
|
||||||
return []
|
return []
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -265,9 +268,13 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
'items': {},
|
'items': {},
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
if not isinstance(field.child, _UnvalidatedField):
|
if not isinstance(field.child, _UnvalidatedField):
|
||||||
mapping['items'] = {
|
map_field = self._map_field(field.child)
|
||||||
"type": self._map_field(field.child).get('type')
|
items = {
|
||||||
|
"type": map_field.get('type')
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
if 'format' in map_field:
|
||||||
|
items['format'] = map_field.get('format')
|
||||||
|
mapping['items'] = items
|
||||||
return mapping
|
return mapping
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# DateField and DateTimeField type is string
|
# DateField and DateTimeField type is string
|
||||||
|
|
@ -337,13 +344,23 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
'type': 'integer'
|
'type': 'integer'
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
self._map_min_max(field, content)
|
self._map_min_max(field, content)
|
||||||
|
# 2147483647 is max for int32_size, so we use int64 for format
|
||||||
|
if int(content.get('maximum', 0)) > 2147483647 or int(content.get('minimum', 0)) > 2147483647:
|
||||||
|
content['format'] = 'int64'
|
||||||
return content
|
return content
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if isinstance(field, serializers.FileField):
|
||||||
|
return {
|
||||||
|
'type': 'string',
|
||||||
|
'format': 'binary'
|
||||||
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Simplest cases, default to 'string' type:
|
# Simplest cases, default to 'string' type:
|
||||||
FIELD_CLASS_SCHEMA_TYPE = {
|
FIELD_CLASS_SCHEMA_TYPE = {
|
||||||
serializers.BooleanField: 'boolean',
|
serializers.BooleanField: 'boolean',
|
||||||
serializers.JSONField: 'object',
|
serializers.JSONField: 'object',
|
||||||
serializers.DictField: 'object',
|
serializers.DictField: 'object',
|
||||||
|
serializers.HStoreField: 'object',
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
return {'type': FIELD_CLASS_SCHEMA_TYPE.get(field.__class__, 'string')}
|
return {'type': FIELD_CLASS_SCHEMA_TYPE.get(field.__class__, 'string')}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -429,13 +446,24 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
schema['maximum'] = int(digits * '9') + 1
|
schema['maximum'] = int(digits * '9') + 1
|
||||||
schema['minimum'] = -schema['maximum']
|
schema['minimum'] = -schema['maximum']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def _get_pagninator(self):
|
def _get_paginator(self):
|
||||||
pagination_class = getattr(self.view, 'pagination_class', None)
|
pagination_class = getattr(self.view, 'pagination_class', None)
|
||||||
if pagination_class:
|
if pagination_class:
|
||||||
return pagination_class()
|
return pagination_class()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
return None
|
return None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def map_parsers(self, path, method):
|
||||||
|
return list(map(attrgetter('media_type'), self.view.parser_classes))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def map_renderers(self, path, method):
|
||||||
|
media_types = []
|
||||||
|
for renderer in self.view.renderer_classes:
|
||||||
|
# BrowsableAPIRenderer not relevant to OpenAPI spec
|
||||||
|
if renderer == renderers.BrowsableAPIRenderer:
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
media_types.append(renderer.media_type)
|
||||||
|
return media_types
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def _get_serializer(self, method, path):
|
def _get_serializer(self, method, path):
|
||||||
view = self.view
|
view = self.view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -455,6 +483,8 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
if method not in ('PUT', 'PATCH', 'POST'):
|
if method not in ('PUT', 'PATCH', 'POST'):
|
||||||
return {}
|
return {}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
self.request_media_types = self.map_parsers(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
serializer = self._get_serializer(path, method)
|
serializer = self._get_serializer(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if not isinstance(serializer, serializers.Serializer):
|
if not isinstance(serializer, serializers.Serializer):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -472,7 +502,7 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
return {
|
return {
|
||||||
'content': {
|
'content': {
|
||||||
ct: {'schema': content}
|
ct: {'schema': content}
|
||||||
for ct in self.content_types
|
for ct in self.request_media_types
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -485,6 +515,8 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
self.response_media_types = self.map_renderers(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
item_schema = {}
|
item_schema = {}
|
||||||
serializer = self._get_serializer(path, method)
|
serializer = self._get_serializer(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -502,7 +534,7 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
'type': 'array',
|
'type': 'array',
|
||||||
'items': item_schema,
|
'items': item_schema,
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
paginator = self._get_pagninator()
|
paginator = self._get_paginator()
|
||||||
if paginator:
|
if paginator:
|
||||||
response_schema = paginator.get_paginated_response_schema(response_schema)
|
response_schema = paginator.get_paginated_response_schema(response_schema)
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
|
|
@ -512,7 +544,7 @@ class AutoSchema(ViewInspector):
|
||||||
'200': {
|
'200': {
|
||||||
'content': {
|
'content': {
|
||||||
ct: {'schema': response_schema}
|
ct: {'schema': response_schema}
|
||||||
for ct in self.content_types
|
for ct in self.response_media_types
|
||||||
},
|
},
|
||||||
# description is a mandatory property,
|
# description is a mandatory property,
|
||||||
# https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#responseObject
|
# https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#responseObject
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ addopts=--tb=short --strict -ra
|
||||||
testspath = tests
|
testspath = tests
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[flake8]
|
[flake8]
|
||||||
ignore = E501
|
ignore = E501,W504
|
||||||
banned-modules = json = use from rest_framework.utils import json!
|
banned-modules = json = use from rest_framework.utils import json!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[isort]
|
[isort]
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
1
setup.py
1
setup.py
|
|
@ -101,6 +101,7 @@ setup(
|
||||||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5',
|
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5',
|
||||||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6',
|
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6',
|
||||||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.7',
|
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.7',
|
||||||
|
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8',
|
||||||
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3 :: Only',
|
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3 :: Only',
|
||||||
'Topic :: Internet :: WWW/HTTP',
|
'Topic :: Internet :: WWW/HTTP',
|
||||||
],
|
],
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -24,8 +24,8 @@ from rest_framework.utils import formatting
|
||||||
from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
from rest_framework.views import APIView
|
||||||
from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet, ModelViewSet
|
from rest_framework.viewsets import GenericViewSet, ModelViewSet
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from . import views
|
|
||||||
from ..models import BasicModel, ForeignKeySource, ManyToManySource
|
from ..models import BasicModel, ForeignKeySource, ManyToManySource
|
||||||
|
from . import views
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
factory = APIRequestFactory()
|
factory = APIRequestFactory()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -5,6 +5,8 @@ from django.utils.translation import gettext_lazy as _
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from rest_framework import filters, generics, pagination, routers, serializers
|
from rest_framework import filters, generics, pagination, routers, serializers
|
||||||
from rest_framework.compat import uritemplate
|
from rest_framework.compat import uritemplate
|
||||||
|
from rest_framework.parsers import JSONParser, MultiPartParser
|
||||||
|
from rest_framework.renderers import JSONRenderer
|
||||||
from rest_framework.request import Request
|
from rest_framework.request import Request
|
||||||
from rest_framework.schemas.openapi import AutoSchema, SchemaGenerator
|
from rest_framework.schemas.openapi import AutoSchema, SchemaGenerator
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -48,6 +50,10 @@ class TestFieldMapping(TestCase):
|
||||||
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.BooleanField()), {'items': {'type': 'boolean'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.BooleanField()), {'items': {'type': 'boolean'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
||||||
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.FloatField()), {'items': {'type': 'number'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.FloatField()), {'items': {'type': 'number'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
||||||
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.CharField()), {'items': {'type': 'string'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.CharField()), {'items': {'type': 'string'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
||||||
|
(serializers.ListField(child=serializers.IntegerField(max_value=4294967295)),
|
||||||
|
{'items': {'type': 'integer', 'format': 'int64'}, 'type': 'array'}),
|
||||||
|
(serializers.IntegerField(min_value=2147483648),
|
||||||
|
{'type': 'integer', 'minimum': 2147483648, 'format': 'int64'}),
|
||||||
]
|
]
|
||||||
for field, mapping in cases:
|
for field, mapping in cases:
|
||||||
with self.subTest(field=field):
|
with self.subTest(field=field):
|
||||||
|
|
@ -71,7 +77,7 @@ class TestOperationIntrospection(TestCase):
|
||||||
method = 'GET'
|
method = 'GET'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
view = create_view(
|
view = create_view(
|
||||||
views.ExampleListView,
|
views.DocStringExampleListView,
|
||||||
method,
|
method,
|
||||||
create_request(path)
|
create_request(path)
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
|
|
@ -80,7 +86,8 @@ class TestOperationIntrospection(TestCase):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
operation = inspector.get_operation(path, method)
|
operation = inspector.get_operation(path, method)
|
||||||
assert operation == {
|
assert operation == {
|
||||||
'operationId': 'listExamples',
|
'operationId': 'listDocStringExamples',
|
||||||
|
'description': 'A description of my GET operation.',
|
||||||
'parameters': [],
|
'parameters': [],
|
||||||
'responses': {
|
'responses': {
|
||||||
'200': {
|
'200': {
|
||||||
|
|
@ -102,23 +109,38 @@ class TestOperationIntrospection(TestCase):
|
||||||
method = 'GET'
|
method = 'GET'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
view = create_view(
|
view = create_view(
|
||||||
views.ExampleDetailView,
|
views.DocStringExampleDetailView,
|
||||||
method,
|
method,
|
||||||
create_request(path)
|
create_request(path)
|
||||||
)
|
)
|
||||||
inspector = AutoSchema()
|
inspector = AutoSchema()
|
||||||
inspector.view = view
|
inspector.view = view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
parameters = inspector._get_path_parameters(path, method)
|
operation = inspector.get_operation(path, method)
|
||||||
assert parameters == [{
|
assert operation == {
|
||||||
'description': '',
|
'operationId': 'RetrieveDocStringExampleDetail',
|
||||||
'in': 'path',
|
'description': 'A description of my GET operation.',
|
||||||
'name': 'id',
|
'parameters': [{
|
||||||
'required': True,
|
'description': '',
|
||||||
'schema': {
|
'in': 'path',
|
||||||
'type': 'string',
|
'name': 'id',
|
||||||
|
'required': True,
|
||||||
|
'schema': {
|
||||||
|
'type': 'string',
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
|
}],
|
||||||
|
'responses': {
|
||||||
|
'200': {
|
||||||
|
'description': '',
|
||||||
|
'content': {
|
||||||
|
'application/json': {
|
||||||
|
'schema': {
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
|
},
|
||||||
},
|
},
|
||||||
}]
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_request_body(self):
|
def test_request_body(self):
|
||||||
path = '/'
|
path = '/'
|
||||||
|
|
@ -364,6 +386,77 @@ class TestOperationIntrospection(TestCase):
|
||||||
},
|
},
|
||||||
}
|
}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def test_parser_mapping(self):
|
||||||
|
"""Test that view's parsers are mapped to OA media types"""
|
||||||
|
path = '/{id}/'
|
||||||
|
method = 'POST'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class View(generics.CreateAPIView):
|
||||||
|
serializer_class = views.ExampleSerializer
|
||||||
|
parser_classes = [JSONParser, MultiPartParser]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
view = create_view(
|
||||||
|
View,
|
||||||
|
method,
|
||||||
|
create_request(path),
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
|
inspector = AutoSchema()
|
||||||
|
inspector.view = view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
request_body = inspector._get_request_body(path, method)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
assert len(request_body['content'].keys()) == 2
|
||||||
|
assert 'multipart/form-data' in request_body['content']
|
||||||
|
assert 'application/json' in request_body['content']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def test_renderer_mapping(self):
|
||||||
|
"""Test that view's renderers are mapped to OA media types"""
|
||||||
|
path = '/{id}/'
|
||||||
|
method = 'GET'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class View(generics.CreateAPIView):
|
||||||
|
serializer_class = views.ExampleSerializer
|
||||||
|
renderer_classes = [JSONRenderer]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
view = create_view(
|
||||||
|
View,
|
||||||
|
method,
|
||||||
|
create_request(path),
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
|
inspector = AutoSchema()
|
||||||
|
inspector.view = view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
responses = inspector._get_responses(path, method)
|
||||||
|
# TODO this should be changed once the multiple response
|
||||||
|
# schema support is there
|
||||||
|
success_response = responses['200']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
assert len(success_response['content'].keys()) == 1
|
||||||
|
assert 'application/json' in success_response['content']
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def test_serializer_filefield(self):
|
||||||
|
path = '/{id}/'
|
||||||
|
method = 'POST'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class ItemSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
|
||||||
|
attachment = serializers.FileField()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class View(generics.CreateAPIView):
|
||||||
|
serializer_class = ItemSerializer
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
view = create_view(
|
||||||
|
View,
|
||||||
|
method,
|
||||||
|
create_request(path),
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
|
inspector = AutoSchema()
|
||||||
|
inspector.view = view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
request_body = inspector._get_request_body(path, method)
|
||||||
|
mp_media = request_body['content']['multipart/form-data']
|
||||||
|
attachment = mp_media['schema']['properties']['attachment']
|
||||||
|
assert attachment['format'] == 'binary'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_retrieve_response_body_generation(self):
|
def test_retrieve_response_body_generation(self):
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
Test that a list of properties is returned for retrieve item views.
|
Test that a list of properties is returned for retrieve item views.
|
||||||
|
|
@ -462,6 +555,22 @@ class TestOperationIntrospection(TestCase):
|
||||||
assert properties['date']['format'] == 'date'
|
assert properties['date']['format'] == 'date'
|
||||||
assert properties['datetime']['format'] == 'date-time'
|
assert properties['datetime']['format'] == 'date-time'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def test_serializer_hstorefield(self):
|
||||||
|
path = '/'
|
||||||
|
method = 'GET'
|
||||||
|
view = create_view(
|
||||||
|
views.ExampleGenericAPIView,
|
||||||
|
method,
|
||||||
|
create_request(path),
|
||||||
|
)
|
||||||
|
inspector = AutoSchema()
|
||||||
|
inspector.view = view
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
responses = inspector._get_responses(path, method)
|
||||||
|
response_schema = responses['200']['content']['application/json']['schema']
|
||||||
|
properties = response_schema['items']['properties']
|
||||||
|
assert properties['hstore']['type'] == 'object'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_serializer_validators(self):
|
def test_serializer_validators(self):
|
||||||
path = '/'
|
path = '/'
|
||||||
method = 'GET'
|
method = 'GET'
|
||||||
|
|
@ -595,3 +704,16 @@ class TestGenerator(TestCase):
|
||||||
assert schema['info']['title'] == 'My title'
|
assert schema['info']['title'] == 'My title'
|
||||||
assert schema['info']['version'] == '1.2.3'
|
assert schema['info']['version'] == '1.2.3'
|
||||||
assert schema['info']['description'] == 'My description'
|
assert schema['info']['description'] == 'My description'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def test_schema_information_empty(self):
|
||||||
|
"""Construction of the top level dictionary."""
|
||||||
|
patterns = [
|
||||||
|
url(r'^example/?$', views.ExampleListView.as_view()),
|
||||||
|
]
|
||||||
|
generator = SchemaGenerator(patterns=patterns)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
request = create_request('/')
|
||||||
|
schema = generator.get_schema(request=request)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
assert schema['info']['title'] == ''
|
||||||
|
assert schema['info']['version'] == ''
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -29,10 +29,35 @@ class ExampleDetailView(APIView):
|
||||||
pass
|
pass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class DocStringExampleListView(APIView):
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
get: A description of my GET operation.
|
||||||
|
post: A description of my POST operation.
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
permission_classes = [permissions.IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def get(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||||
|
pass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||||
|
pass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class DocStringExampleDetailView(APIView):
|
||||||
|
permission_classes = [permissions.IsAuthenticatedOrReadOnly]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def get(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
A description of my GET operation.
|
||||||
|
"""
|
||||||
|
pass
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Generics.
|
# Generics.
|
||||||
class ExampleSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
|
class ExampleSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
|
||||||
date = serializers.DateField()
|
date = serializers.DateField()
|
||||||
datetime = serializers.DateTimeField()
|
datetime = serializers.DateTimeField()
|
||||||
|
hstore = serializers.HStoreField()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class ExampleGenericAPIView(generics.GenericAPIView):
|
class ExampleGenericAPIView(generics.GenericAPIView):
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -1080,6 +1080,7 @@ class TestDecimalField(FieldValues):
|
||||||
invalid_inputs = (
|
invalid_inputs = (
|
||||||
('abc', ["A valid number is required."]),
|
('abc', ["A valid number is required."]),
|
||||||
(Decimal('Nan'), ["A valid number is required."]),
|
(Decimal('Nan'), ["A valid number is required."]),
|
||||||
|
(Decimal('Snan'), ["A valid number is required."]),
|
||||||
(Decimal('Inf'), ["A valid number is required."]),
|
(Decimal('Inf'), ["A valid number is required."]),
|
||||||
('12.345', ["Ensure that there are no more than 3 digits in total."]),
|
('12.345', ["Ensure that there are no more than 3 digits in total."]),
|
||||||
(200000000000.0, ["Ensure that there are no more than 3 digits in total."]),
|
(200000000000.0, ["Ensure that there are no more than 3 digits in total."]),
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -494,28 +494,28 @@ class CustomPermissionsTests(TestCase):
|
||||||
self.custom_message = 'Custom: You cannot access this resource'
|
self.custom_message = 'Custom: You cannot access this resource'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_permission_denied(self):
|
def test_permission_denied(self):
|
||||||
response = denied_view(self.request, pk=1)
|
response = denied_view(self.request, pk=1)
|
||||||
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
||||||
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
||||||
self.assertNotEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
self.assertNotEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_permission_denied_with_custom_detail(self):
|
def test_permission_denied_with_custom_detail(self):
|
||||||
response = denied_view_with_detail(self.request, pk=1)
|
response = denied_view_with_detail(self.request, pk=1)
|
||||||
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
||||||
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
||||||
self.assertEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
self.assertEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_permission_denied_for_object(self):
|
def test_permission_denied_for_object(self):
|
||||||
response = denied_object_view(self.request, pk=1)
|
response = denied_object_view(self.request, pk=1)
|
||||||
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
||||||
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
||||||
self.assertNotEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
self.assertNotEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def test_permission_denied_for_object_with_custom_detail(self):
|
def test_permission_denied_for_object_with_custom_detail(self):
|
||||||
response = denied_object_view_with_detail(self.request, pk=1)
|
response = denied_object_view_with_detail(self.request, pk=1)
|
||||||
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
detail = response.data.get('detail')
|
||||||
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, status.HTTP_403_FORBIDDEN)
|
||||||
self.assertEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
self.assertEqual(detail, self.custom_message)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class PermissionsCompositionTests(TestCase):
|
class PermissionsCompositionTests(TestCase):
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ class TestHyperlinkedIdentityField(APISimpleTestCase):
|
||||||
def test_improperly_configured(self):
|
def test_improperly_configured(self):
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
If a matching view cannot be reversed with the given instance,
|
If a matching view cannot be reversed with the given instance,
|
||||||
the the user has misconfigured something, as the URL conf and the
|
the user has misconfigured something, as the URL conf and the
|
||||||
hyperlinked field do not match.
|
hyperlinked field do not match.
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
self.field.reverse = fail_reverse
|
self.field.reverse = fail_reverse
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -555,7 +555,7 @@ class TestDefaultOutput:
|
||||||
bar = serializers.CharField(source='foo.bar', allow_null=True)
|
bar = serializers.CharField(source='foo.bar', allow_null=True)
|
||||||
optional = serializers.CharField(required=False, allow_null=True)
|
optional = serializers.CharField(required=False, allow_null=True)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# allow_null=True should imply default=None when serialising:
|
# allow_null=True should imply default=None when serializing:
|
||||||
assert Serializer({'foo': None}).data == {'foo': None, 'bar': None, 'optional': None, }
|
assert Serializer({'foo': None}).data == {'foo': None, 'bar': None, 'optional': None, }
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
4
tox.ini
4
tox.ini
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ envlist =
|
||||||
{py35,py36,py37}-django20,
|
{py35,py36,py37}-django20,
|
||||||
{py35,py36,py37}-django21
|
{py35,py36,py37}-django21
|
||||||
{py35,py36,py37}-django22
|
{py35,py36,py37}-django22
|
||||||
{py36,py37}-djangomaster,
|
{py36,py37,py38}-djangomaster,
|
||||||
base,dist,lint,docs,
|
base,dist,lint,docs,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[travis:env]
|
[travis:env]
|
||||||
|
|
@ -44,14 +44,12 @@ deps =
|
||||||
-rrequirements/requirements-optionals.txt
|
-rrequirements/requirements-optionals.txt
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[testenv:lint]
|
[testenv:lint]
|
||||||
basepython = python3.7
|
|
||||||
commands = ./runtests.py --lintonly
|
commands = ./runtests.py --lintonly
|
||||||
deps =
|
deps =
|
||||||
-rrequirements/requirements-codestyle.txt
|
-rrequirements/requirements-codestyle.txt
|
||||||
-rrequirements/requirements-testing.txt
|
-rrequirements/requirements-testing.txt
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[testenv:docs]
|
[testenv:docs]
|
||||||
basepython = python3.7
|
|
||||||
skip_install = true
|
skip_install = true
|
||||||
commands = mkdocs build
|
commands = mkdocs build
|
||||||
deps =
|
deps =
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user