This commit introduces several improvements to the template tags and filters used in Django Rest Framework (DRF). The enhancements focus on code readability, maintainability, efficiency, and security. Key changes include: ### Enhancements: 1. **Regex Precompilation:** - Moved regular expression compilation outside of functions to avoid recompilation and improve performance. 2. **Simplified Add Class Function:** - Refactored the `add_class` function for better readability and efficiency, ensuring that CSS classes are added accurately and safely. 3. **Modularized and Documented Code:** - Broke down larger functions and added detailed comments and docstrings to explain the purpose and functionality of each tag and filter, improving code maintainability. 4. **Security Enhancements:** - Ensured proper escaping of HTML and judicious use of `mark_safe` to prevent XSS attacks, particularly in functions dealing with user-generated content. 5. **Optimized Markdown Rendering:** - Added conditional checks for the availability of the `apply_markdown` function and provided safe fallbacks, enhancing the robustness of markdown rendering. 6. **Improved Handling of Dynamic URLs and Headers:** - Enhanced the logic for handling dynamic URLs and long headers, ensuring that URLs are quoted correctly and headers are broken safely to maintain readability. ### Detailed Changes: - Precompiled regex patterns for class handling and URL validation. - Simplified the `add_class` logic by reducing regex operations and ensuring accurate class insertion. - Added docstrings and inline comments for better code understanding. - Enhanced security by using `escape` and `mark_safe` appropriately. - Improved the handling of markdown text rendering by checking for `apply_markdown` and using `mark_safe`. - Refined the handling of pagination HTML and form rendering for better user experience. - Optimized functions to ensure better performance and adherence to Django best practices. These changes aim to enhance the overall functionality, readability, and security of the template tags and filters, contributing to a more robust and maintainable codebase for Django Rest Framework. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| .tx | ||
| docs | ||
| docs_theme | ||
| licenses | ||
| requirements | ||
| rest_framework | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .pre-commit-config.yaml | ||
| codecov.yml | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| LICENSE.md | ||
| MANIFEST.in | ||
| mkdocs.yml | ||
| PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| runtests.py | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
| setup.cfg | ||
| setup.py | ||
| tox.ini | ||
Django REST framework
Awesome web-browsable Web APIs.
Full documentation for the project is available at https://www.django-rest-framework.org/.
Funding
REST framework is a collaboratively funded project. If you use REST framework commercially we strongly encourage you to invest in its continued development by signing up for a paid plan.
The initial aim is to provide a single full-time position on REST framework. Every single sign-up makes a significant impact towards making that possible.
Many thanks to all our wonderful sponsors, and in particular to our premium backers, Sentry, Stream, Spacinov, Retool, bit.io, PostHog, CryptAPI, FEZTO, Svix, and Zuplo.
Overview
Django REST framework is a powerful and flexible toolkit for building Web APIs.
Some reasons you might want to use REST framework:
- The Web browsable API is a huge usability win for your developers.
- Authentication policies including optional packages for OAuth1a and OAuth2.
- Serialization that supports both ORM and non-ORM data sources.
- Customizable all the way down - just use regular function-based views if you don't need the more powerful features.
- Extensive documentation, and great community support.
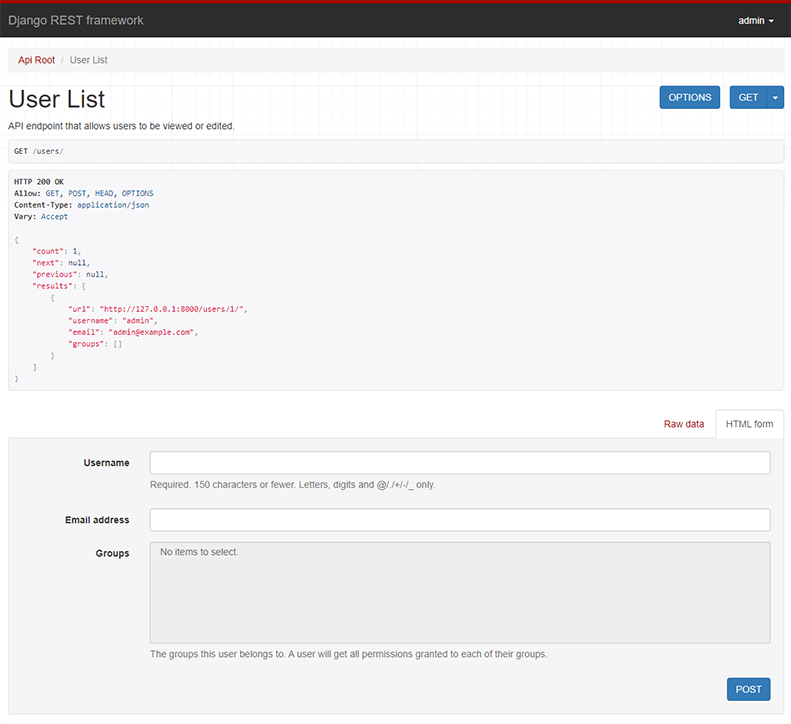
Below: Screenshot from the browsable API
Requirements
- Python 3.8+
- Django 5.0, 4.2
We highly recommend and only officially support the latest patch release of each Python and Django series.
Installation
Install using pip...
pip install djangorestframework
Add 'rest_framework' to your INSTALLED_APPS setting.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'rest_framework',
]
Example
Let's take a look at a quick example of using REST framework to build a simple model-backed API for accessing users and groups.
Startup up a new project like so...
pip install django
pip install djangorestframework
django-admin startproject example .
./manage.py migrate
./manage.py createsuperuser
Now edit the example/urls.py module in your project:
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.urls import include, path
from rest_framework import routers, serializers, viewsets
# Serializers define the API representation.
class UserSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ['url', 'username', 'email', 'is_staff']
# ViewSets define the view behavior.
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
queryset = User.objects.all()
serializer_class = UserSerializer
# Routers provide a way of automatically determining the URL conf.
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', UserViewSet)
# Wire up our API using automatic URL routing.
# Additionally, we include login URLs for the browsable API.
urlpatterns = [
path('', include(router.urls)),
path('api-auth/', include('rest_framework.urls', namespace='rest_framework')),
]
We'd also like to configure a couple of settings for our API.
Add the following to your settings.py module:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
... # Make sure to include the default installed apps here.
'rest_framework',
]
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# Use Django's standard `django.contrib.auth` permissions,
# or allow read-only access for unauthenticated users.
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [
'rest_framework.permissions.DjangoModelPermissionsOrAnonReadOnly',
]
}
That's it, we're done!
./manage.py runserver
You can now open the API in your browser at http://127.0.0.1:8000/, and view your new 'users' API. If you use the Login control in the top right corner you'll also be able to add, create and delete users from the system.
You can also interact with the API using command line tools such as curl. For example, to list the users endpoint:
$ curl -H 'Accept: application/json; indent=4' -u admin:password http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/
[
{
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/1/",
"username": "admin",
"email": "admin@example.com",
"is_staff": true,
}
]
Or to create a new user:
$ curl -X POST -d username=new -d email=new@example.com -d is_staff=false -H 'Accept: application/json; indent=4' -u admin:password http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/
{
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/2/",
"username": "new",
"email": "new@example.com",
"is_staff": false,
}
Documentation & Support
Full documentation for the project is available at https://www.django-rest-framework.org/.
For questions and support, use the REST framework discussion group, or #restframework on libera.chat IRC.
Security
Please see the security policy.