5.6 KiB
source: pagination.py
Pagination
Django provides a few classes that help you manage paginated data – that is, data that’s split across several pages, with “Previous/Next” links.
REST framework includes support for customizable pagination styles. This allows you to modify how large result sets are split into individual pages of data.
The pagination API can support either:
- Pagination links that are provided as part of the content of the response.
- Pagination links that are included in response headers, such as
Content-RangeorLink.
The built-in styles currently all use links included as part of the content of the response. This style is more accessible when using the browsable API.
Pagination is only performed automatically if you're using the generic views or viewsets. If you're using a regular APIView, you'll need to call into the pagination API yourself to ensure you return a paginated response. See the source code for the mixins.ListMixin and generics.GenericAPIView classes for an example.
Setting the pagination style
The default pagination style may be set globally, using the DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS settings key. For example, to use the built-in limit/offset pagination, you would do:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'rest_framework.pagination.LimitOffsetPagination'
}
You can also set the pagination class on an individual view by using the pagination_class attribute. Typically you'll want to use the same pagination style throughout your API, although you might want to vary individual aspects of the pagination, such as default or maximum page size, on a per-view basis.
Modifying the pagination style
If you want to modify particular aspects of the pagination style, you'll want to override one of the pagination classes, and set the attributes that you want to change.
class LargeResultsSetPagination(PageNumberPagination):
paginate_by = 1000
paginate_by_param = 'page_size'
max_paginate_by = 10000
class StandardResultsSetPagination(PageNumberPagination):
paginate_by = 100
paginate_by_param = 'page_size'
max_paginate_by = 1000
You can then apply your new style to a view using the .pagination_class attribute:
class BillingRecordsView(generics.ListAPIView):
queryset = Billing.objects.all()
serializer = BillingRecordsSerializer
pagination_class = LargeResultsSetPagination
Or apply the style globally, using the DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS settings key. For example:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'apps.core.pagination.StandardResultsSetPagination'
}
API Reference
PageNumberPagination
LimitOffsetPagination
Custom pagination styles
To create a custom pagination serializer class you should subclass pagination.BasePagination and override the paginate_queryset(self, queryset, request, view=None) and get_paginated_response(self, data) methods:
- The
paginate_querysetmethod is passed the initial queryset and should return an iterable object that contains only the data in the requested page. - The
get_paginated_responsemethod is passed the serialized page data and should return aResponseinstance.
Note that the paginate_queryset method may set state on the pagination instance, that may later be used by the get_paginated_response method.
Example
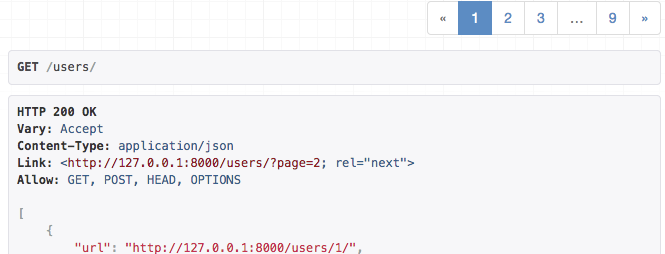
Let's modify the built-in PageNumberPagination style, so that instead of include the pagination links in the body of the response, we'll instead include a Link header, in a similar style to the GitHub API.
class LinkHeaderPagination(pagination.PageNumberPagination):
def get_paginated_response(self, data):
next_url = self.get_next_link()
previous_url = self.get_previous_link()
if next_url is not None and previous_url is not None:
link = '<{next_url}; rel="next">, <{previous_url}; rel="prev">'
elif next_url is not None:
link = '<{next_url}; rel="next">'
elif previous_url is not None:
link = '<{previous_url}; rel="prev">'
else:
link = ''
link = link.format(next_url=next_url, previous_url=previous_url)
headers = {'Link': link} if link else {}
return Response(data, headers=headers)
Using your custom pagination class
To have your custom pagination class be used by default, use the DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS setting:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_PAGINATION_CLASS': 'my_project.apps.core.pagination.LinkHeaderPagination',
'PAGINATE_BY': 10
}
API responses for list endpoints will now include a Link header, instead of including the pagination links as part of the body of the response, for example:
A custom pagination style, using the 'Link' header'
Third party packages
The following third party packages are also available.
DRF-extensions
The DRF-extensions package includes a PaginateByMaxMixin mixin class that allows your API clients to specify ?page_size=max to obtain the maximum allowed page size.